All Articles
Trending Articles

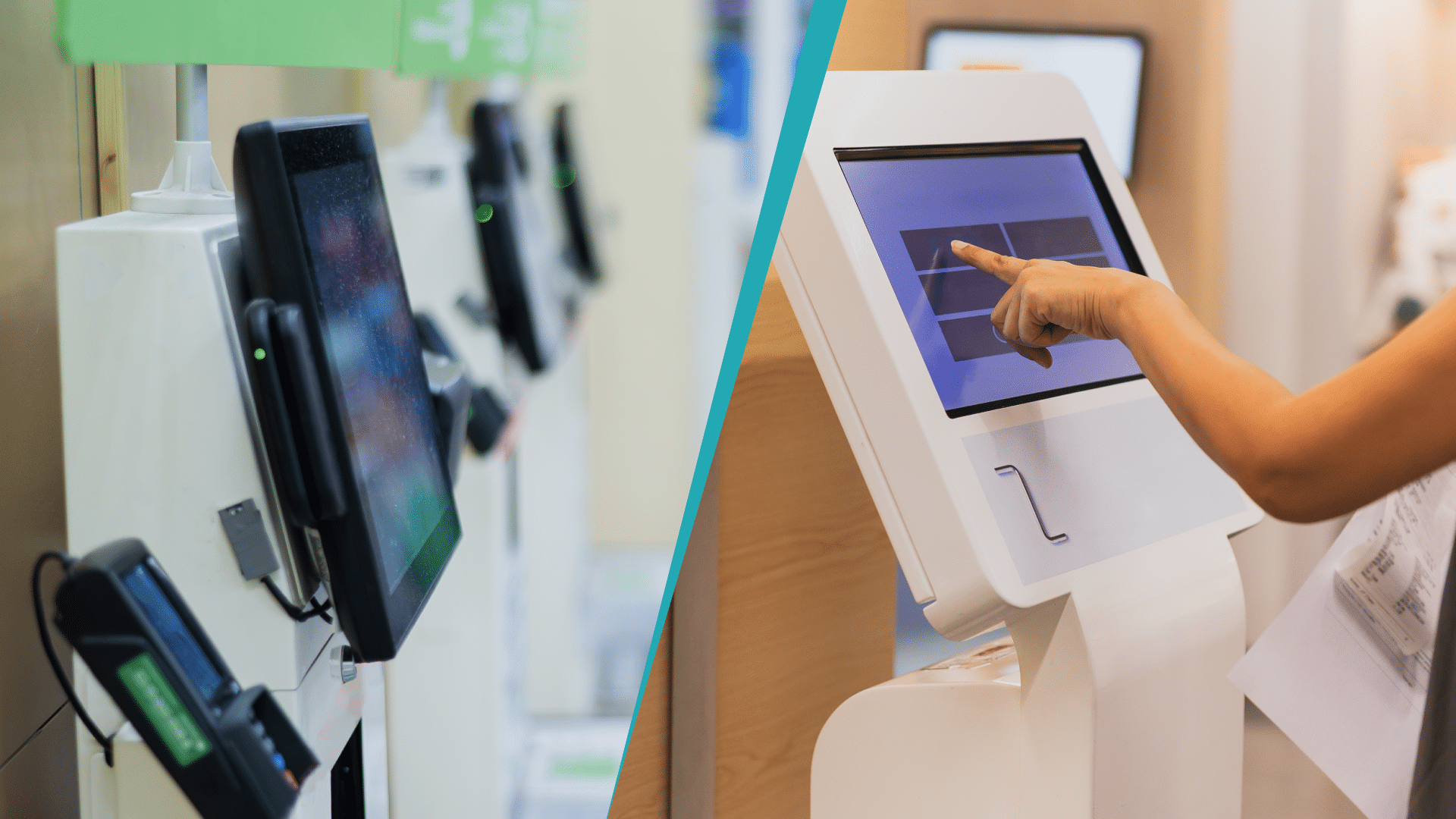
What Is a POS System and How Does it Work? Everything You Need to Know
A point of sale (POS) system used to be a cash register that simply recorded the day’s sales and organized your cash into sections. With today’s technology, however, a POS ...
Best Point Of Sale Systems

What Is a Sales Growth Calculator? How It Works and Why It Matters
What is Sales Growth? A Sales Growth Calculator is an analytical tool that quantifies the percentage increase in sales revenue over a defined period. Beyond simple tracking, it leverages historical ...
Point of sale Solution Alternatives

Bottle POS Review 2025: Overview, Features, Pricing, Pros and Cons
💡 Key Takeaways: Looking for an in-depth look at Bottle POS? This Bottle POS review will cover everything you need to know about the point of sale system in 2025, ...
Point Of sale Product Comparisons
Zettle vs. Square: Which POS Solution Should You Use to Take Payments for Your Business in 2025?
If you’re considering Zettle vs Square, you’re likely looking for an affordable and user-friendly solution to process payments and manage sales. Zettle and Square offer card readers, mobile POS apps, ...
Point of sale Product Pricing Guides
Measure Retail Profit Easily with a Sales Margin Calculator
Want to know how profitable your business really is? A sales margin calculator is the tool you need to measure your profit margins quickly and accurately. This blog explores what ...
Testimonials

Bottle POS Review 2025: Overview, Features, Pricing, Pros and Cons
💡 Key Takeaways: Looking for an in-depth look at Bottle POS? This Bottle POS review will cover everything you need to know about the point of sale system in 2025, ...
Inventory Management

Measure Retail Profit Easily with a Sales Margin Calculator
Want to know how profitable your business really is? A sales margin calculator is the tool you need to measure your profit margins quickly and accurately. This blog explores what ...
Credit Card and Payment Processing

Clover Fee Calculator: Instantly Estimate Your Monthly POS Costs
What Are Clover POS Fees? Below, we explore Clover POS pricing, including Clover’s hardware costs, software subscription plans, payment processing fees, and add-on costs. Clover Hardware Fees Hardware can be ...
Point of Sale Features and Tools

Measure Retail Profit Easily with a Sales Margin Calculator
Want to know how profitable your business really is? A sales margin calculator is the tool you need to measure your profit margins quickly and accurately. This blog explores what ...
Downloadable eBooks and Guides

The KORONA Studio Back Office Guidebook

Understanding Credit Card Processing eGuide

A Guide On How To Be A Great Retail Manager
Testimonials
"I’ve never worked with a company that has been as focused on customer service. When we call you guys the response has been phenomenal If I could just choose companies based on how they provide customer service, you’d be the top of my list."
– Jennifer from Duplin Winery
Find the Right POS Solution for Your Business