In today’s fast-paced and data-driven world, retail businesses seek innovative solutions to streamline operations, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance efficiency. Among these solutions, fixed RFID readers have emerged as a game-changer.
Fixed RFID readers, equipped with advanced technology and unmatched capabilities, offer businesses a powerful tool to capture and process data from RFID tags in a stationary location. These readers enable automated and real-time tracking, providing enhanced visibility into inventory, assets, and products throughout the supply chain.
Fixed RFID readers have revolutionized how businesses monitor, manage, and optimize their operations. From warehouses and manufacturing facilities to retail stores and distribution centers, their popularity is gaining more and more traction. Below is a detailed article about their use in the retail world and how businesses can adopt the rising technology.

What Is RFID Technology?
RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data between a reader and special tags wirelessly. This allows for the identification, locating, and tracking of various objects or assets.
Readers have three main components: an antenna, a transceiver, and a processor. The antenna emits radio waves and receives signals from the RFID tags. At the same time, the transceiver converts the received radio signals into processable data. The processor then analyzes the data, performs the necessary actions, or sends it to a central system.
RFID technology differs from typical barcode tracking systems because they don’t require a direct line of sight. That means retailers can scan dozens of inventory items simultaneously without unboxing.
What Is A Fixed RFID Reader?
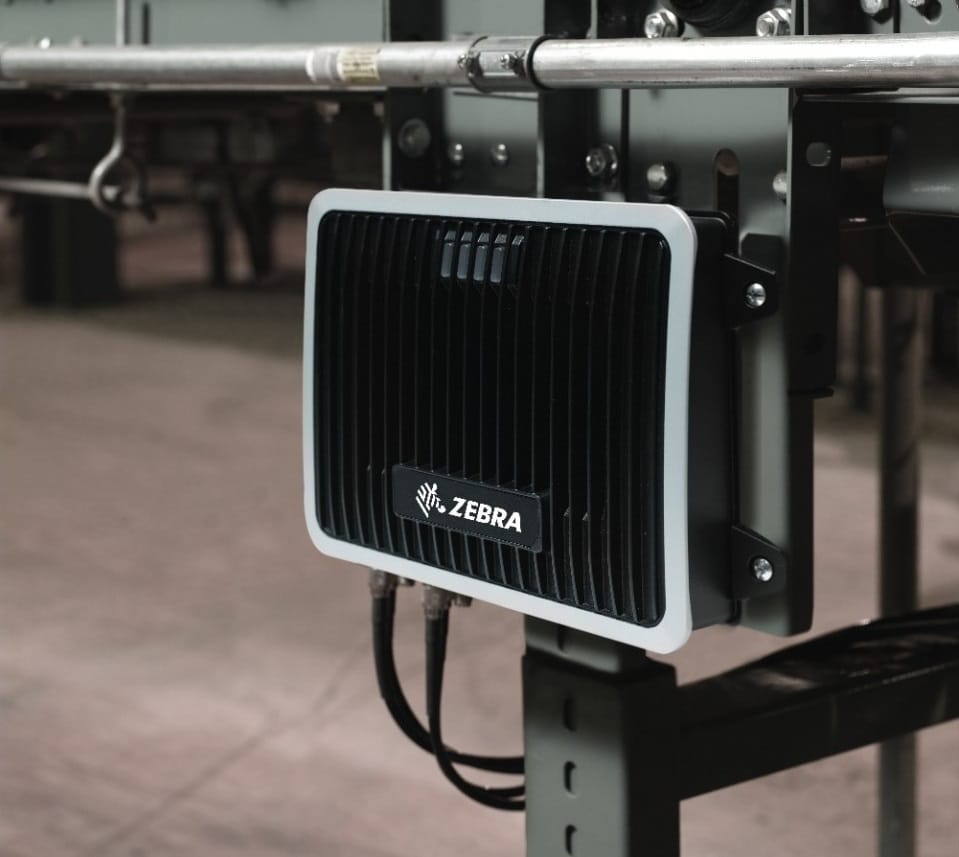
Fixed RFID readers capture and process tag data from a stationary location. Businesses typically install them strategically in warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and retail stores. Any place where consistent and accurate tracking of items is essential is a good place for fixed RFID use.
These readers look like modems. Inventory managers typically mount them on walls, ceilings, or other fixed structures for optimal coverage and performance.
What Are The Advantages Of Fixed RFID Readers?
Fixed RFID readers offer several advantages. First, they enable automated and real-time inventory tracking throughout the supply chain. This feature improves operational efficiency, reduces manual labor, and minimizes errors associated with manual data entry.
Second, they provide improved traceability, allowing businesses to monitor the movement and location of items. This visibility aids in inventory management, replenishment, and loss prevention.
Third, fixed RFID readers offer faster and more reliable data capture than traditional barcode scanning. Employees can read multiple tags simultaneously as long as they are within the reader’s range.
Moreover, fixed RFID readers integrate with other systems, such as inventory management software or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This cohesion streamlines data integration and enhances overall business processes. Some retail companies even combine their RFID with additional technologies to enable advanced functionalities, such as temperature monitoring or tamper detection.
Here are some more details on specific ways that retailers utilize fixed RFID readers:
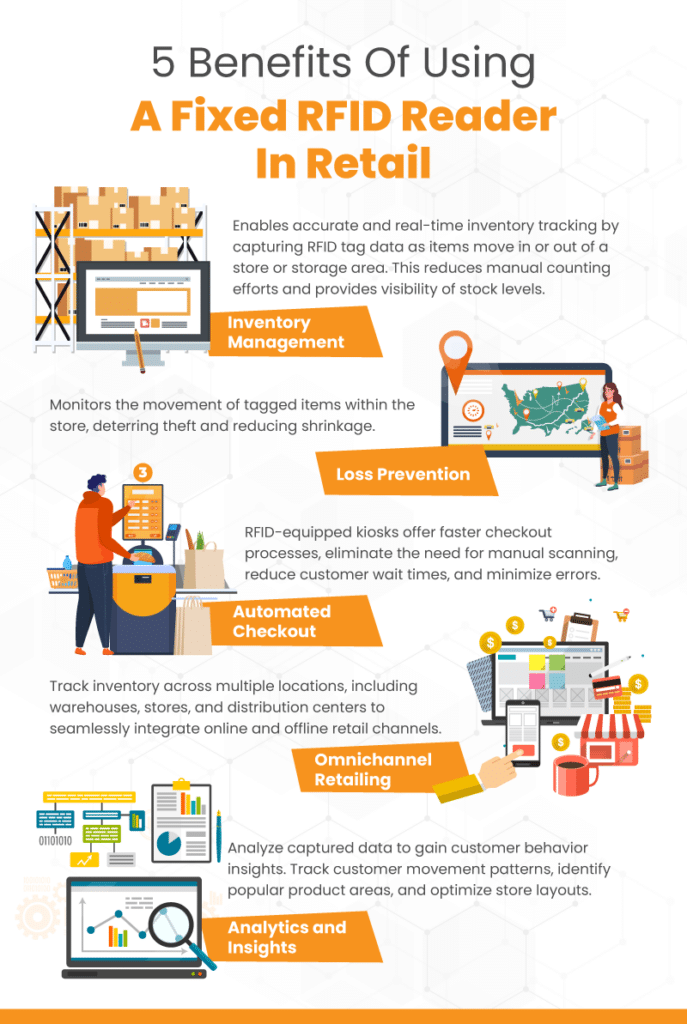
Inventory Management
Fixed RFID readers enable accurate and real-time inventory tracking. By placing readers at store entrances, exits, or storage areas, retailers can capture RFID tag data as items move in or out of a store. This provides visibility into stock levels, reduces manual counting efforts, and helps prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
Also, as tagged items reach a certain threshold, the reader sends alerts to store associates. With automated inventory management, retailers can optimize restocking, improve demand forecasting, and ensure product availability on shelves.
Loss Prevention
Fixed RFID readers aid in loss prevention efforts by monitoring the movement of tagged items within the store. For example, a high-end liquor store might utilize fixed RFID readers to prevent theft and monitor inventory movement. Once each item in the store is tagged, retailers can position fixed readers at store entrances and exits.
Suppose a tagged item passes through an exit without being properly purchased or deactivated. In that case, the reader can trigger alarms or alerts, notifying store personnel of potential theft. This feature helps deter shoplifting and reduces shrinkage, thereby improving profit margins.
Omnichannel Retailing
Fixed RFID readers enable seamless integration between online and offline retail channels. By tagging products with RFID, retailers can track inventory across multiple locations, including warehouses, stores, and distribution centers.
Fixed readers capture the tag data as items are received, shipped, or transferred, ensuring accurate inventory visibility across the supply chain. This facilitates efficient order fulfillment and buy online pick up in-store options. Plus, it improves accuracy in eCommerce product availability.
Analytics and Insights
Retailers can analyze the data captured by fixed RFID to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, product performance, and store operations. Retailers can also track customer movement patterns, identify popular product areas, and optimize store layouts. These factors help business owners make data-driven decisions to power merchandising strategies and even plan marketing and promotional campaigns.
Automated Checkout
RFID-equipped kiosks are the future of self-checkout. First, retail workers embed RFID tags in each product. Then, as customers place their items on a conveyor belt or in a basket, the fixed readers automatically capture the tag data. Thus, RFID kiosks offer faster checkout processes, eliminate the need for manual scanning, reduce customer wait times, and minimize errors.

Fixed RFID Reader Price Range
The cost of retail fixed RFID readers varies depending on the brand, model, features, and the retailer’s requirements. Generally, fixed RFID readers can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars per unit.
Entry-level fixed RFID readers with basic functionality and lower read range capabilities are the most affordable. They are priced around $200 to $500 per reader. These readers are suitable for small-scale retail environments with limited read range requirements.
Mid-range fixed RFID readers offer higher performance, better read range, and additional features such as multiple antenna ports or connectivity options. These range from $500 to $1,500 per unit. These readers suit medium-sized retail operations or stores with more advanced inventory management needs.
High-end fixed RFID readers equipped with advanced features like multiple protocol support, integrated sensors, or rugged designs. They cost anywhere from $1,500 to $5,000 per reader. These readers are prevalent in large enterprise retail operations, distribution centers, or industrial settings where durability, reliability, and extended read range capabilities are crucial.
Additional Components and Costs
It’s important to note that the cost of fixed RFID readers is just one component of the overall implementation cost. Additional costs may include RFID tags, installation, software integration, antennas, cables, and any required customization or support services. The total cost of a retail RFID system will depend on the deployment scale, the requirements’ complexity, and any additional hardware or software needed.
Set Up Your Fixed RFID Reader Today With KORONA POS
KORONA POS inventory management system is specifically designed for businesses dealing with extensive and intricate product catalogs. The solution provides a comprehensive set of features, including ABC analysis, stock-level optimization, and automated reordering. Plus, the platform is fully integrated with RFID solutions.
Get in touch now to discover how we can assist you in implementing RFID technology in your warehouse or retail store. The experienced technicians at KORONA POS will guide you through selecting the optimal hardware and software solutions tailored to your specific industry and market segment. Sign up for a demo to learn more by clicking the button below!
FAQs: Fixed RFID Readers
There are two main types of RFID readers, fixed and mobile. Fixed RFID readers are mounted to a wall or shelf and monitor the movement of RFID tags in a store or warehouse. Mobile RFID readers are generally handheld and used to scan items, similar to a barcode.
Fixed RFID readers are stationary devices that are typically mounted on walls, shelves, or entryways. They are designed for continuous and automated monitoring of RFID tags within their range, providing real-time data capture and tracking. In retail, fixed RFID readers are used in inventory management, loss prevention, and emerging checkout technologies.
The main difference between fixed and mobile RFID readers lies in their mobility and location. Fixed RFID readers are stationary devices installed in specific locations, while mobile RFID readers are portable and can be carried around. Mobile RFID readers offer flexibility for on-the-go applications like reading RFID tags in different areas, whereas fixed readers are suitable for continuous and automated monitoring in a specific location.