Struggling with inventory errors, stockouts, or long checkout lines? Fortunately, RFID implementation in retail offers an innovative solution to modernize your operations.
In this guide, we’ll explain how to implement RFID in your retail business step by step. From choosing the right hardware to training your staff, you’ll learn everything you need to execute a successful RFID strategy and stay successful.
💡 Key Takeaways:
- RFID automates inventory tracking, enabling real-time stock monitoring and reducing manual errors.
- A step-by-step approach, from defining your objectives to piloting and monitoring, facilitates your transition.
- RFID offers long-term return on investment through improved customer experience, faster checkouts, and smarter logistics.
What is RFID Implementation?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) implementation refers to the process of integrating RFID technology into your retail operations. This includes tagging items with RFID chips, installing readers, and syncing the data to software platforms for real-time inventory management, analytics, and automation.
9 Steps to Implement RFID in Your Retail Business
Implementing RFID involves strategic planning, hardware and software selection, testing, and training. Each step builds on the last to ensure your long-term success.
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Start by identifying what you want RFID to achieve. Goals may include reducing inventory inaccuracies, enhancing theft prevention, improving supply chain visibility, or automating checkouts.
Using clear key performance indicators (KPIs) will help you measure success post-implementation.
2. Assess Store Infrastructure
Evaluate your current technology and physical store layout.
Are your shelves and POS systems compatible with RFID readers? Can your Wi-Fi handle the data load? An infrastructure audit can help facilitate a smooth deployment.
3. Develop an RFID Tagging Strategy
Not every product needs a tag. Decide which SKUs offer the most value from tracking. Determine where tags will be placed (on packaging, inside labels, etc.) and whether passive or active tags make the most sense.
4. Select the Right RFID Technology
Consider factors like RFID cost, tag type , frequency (low, high, or ultra-high), and read range. Additionally, select RFID readers and antennas that fit the store layout and operational needs.
Fixed Vs. Mobile Readers
↪ Fixed RFID Readers
These are installed in specific zones (entryways, shelves, backrooms) and offer continuous, automated tracking without staff involvement.
↪ Mobile RFID Readers
Handheld or cart-mounted devices provide flexible tracking. They’re useful for inventory checks, returns, or spot audits without fixed installation.
Feature | Fixed RFID Readers | Mobile RFID Readers |
Installation | Installed at specific locations (doorways, coveyers, etc.) | Handheld or mounted on carts; portable |
Mobility | Stationary; cannot be moved easily | Portable; can be carried to different locations |
Use Case | Ideal for automated tracking in high-traffic zones | Best for spot-checks, inventory audits, or fieldwork |
Connectivity | Often hardwired or uses fixed network connections | Connects via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular |
Range & Coverage | Higher read range | Shorter range |
Cost | Higher upfront cost (equipment + installation) | Lower upfront cost (no installation required) |
Data Collection Mode | Continuous/automated scanning | Manual/triggered scanning |
Typical Environments | Warehouses, loading docks, manufacturing lines | Retail stores, libraries, healthcare, field inspections |
5. RFID Hardware
Retailers must choose the type of RFID hardware that best suits their operation. Here are the main options:
↪ RFID Tags
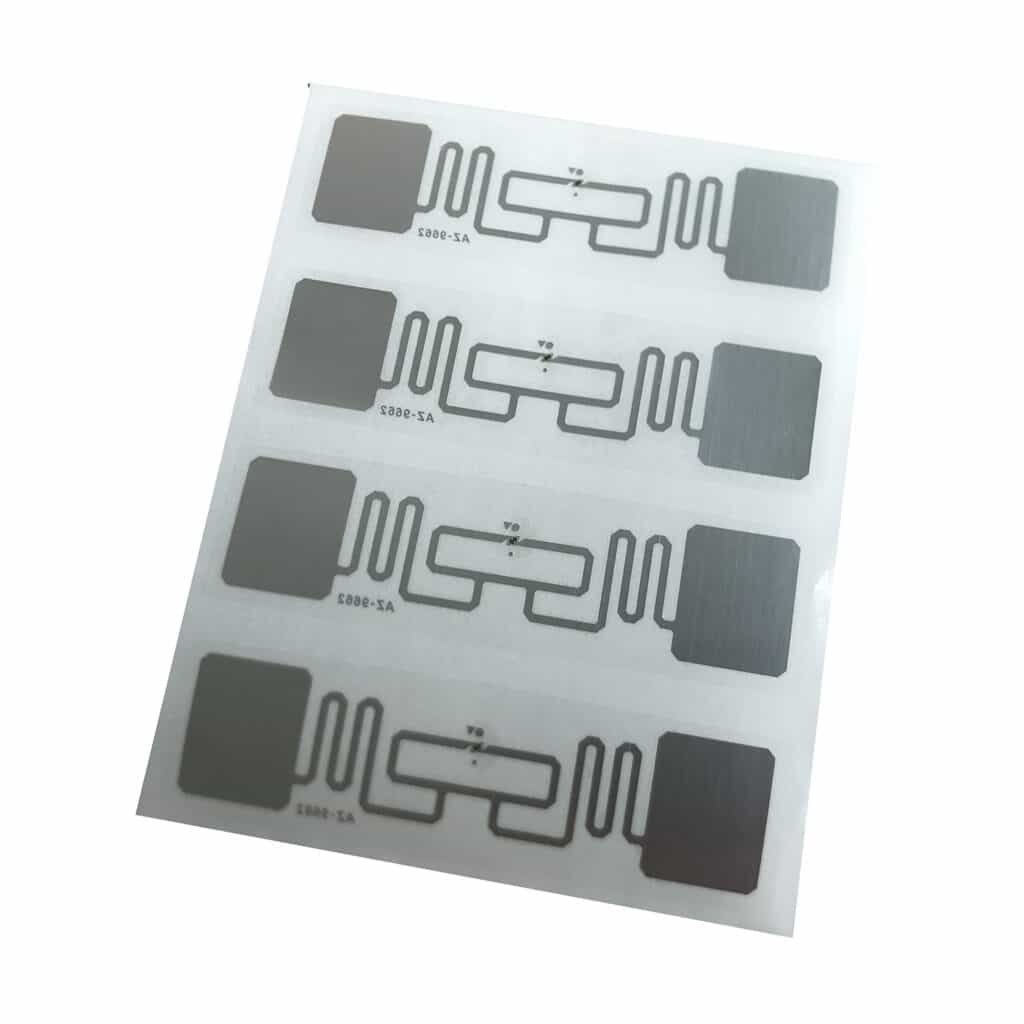
These tiny chips store product info and transmit it via radio waves. They can be passive (powered by the reader) or active (battery-powered).
↪ RFID Reader
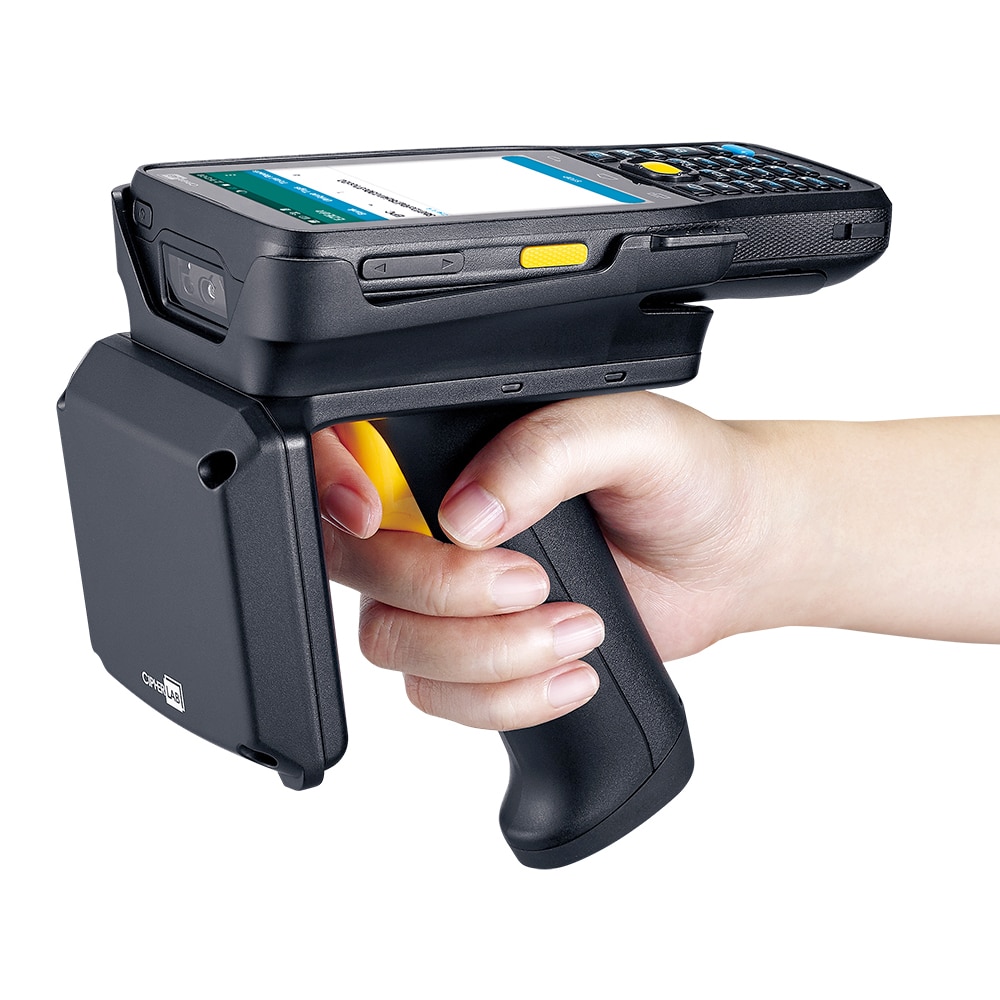

An RFID reader is the core device that communicates with tags to gather data.It allows for on-the-go scanning, item locating, and data capture from RFID tags.
↪ Antenna

An RFID antenna works with readers to emit and receive radio signals. Placement is key for comprehensive coverage and accurate reads.
6. RFID Software
Your hardware will communicate through the middleware with a software system. RFID software typically contains the following:
↪ RFID Platform
This software manages the data collected from the RFID readers and tags. It typically includes tag encoding, data filtering, real-time monitoring, and reporting.
↪ Database
The RFID system requires a database to store the collected data, including tag IDs, timestamps, and location information.
↪ Middleware
Connects RFID hardware to your backend systems. It filters, processes, and transfers data to inventory platforms and databases.
↪ Application Software
Specific programs interpret the RFID data for various purposes, such as inventory management, asset tracking, access control, and supply chain optimization.
↪ Integration with Existing Systems
To fully leverage RFID’s capabilities, integrate the technology with existing retail systems such as inventory management solutions and point of sale. The best retail point of sale systems will have this integration capability.

7. Conduct a Pilot Study on Your RFID Implementation
Start with a small-scale rollout in one store of section before rolling out RFID across the entire retail chain. This approach lets retailers test the technology, understand challenges, and fine-tune their process.
8. Train Staff and Foster Employee Engagement
Gaining staff buy-in is essential for long-term success and accurate data capture. Educate them about the benefits of RFID, demonstrate how to use the systems, and explain how it can improve day-to-day operations.
9. Monitor RFID Performance
Once RFID implementation is complete, regularly monitor and evaluate its performance against the defined goals and objectives. Use KPIs to measure the impact of RFID on inventory management, sales, and customer satisfaction.
Inventory management a headache?
KORONA POS makes stock control easy. Automate tasks, generate custom reports, and learn how you can start improving your business.
Main Benefits of RFID Implementation
RFID implementation in retail offers numerous benefits that can significantly improve operational efficiency, customer experience, and profitability. Here are four key advantages:
📊 Benefit #1: Enhanced Inventory Management
Unlike barcodes, RFID technology allows retailers to scan multiple items at once without needing a direct line of sight, making stocktaking faster and easier. With better insight into inventory levels and locations, retailers can automatically restock items, avoiding stockouts and excess stock.
🚚 Benefit #2: Efficient Supply Chain and Logistics
With RFID, products move faster and with more transparency from warehouse to shelf. Retailers can monitor product movement through every stage, thus improving shipment accuracy and reducing errors.
🛒 Benefit #3: Better Customer Experience
With RFID-enabled self-checkout, customers can easily scan and pay for their items, enhancing their shopping experience to be both innovative and extremely convenient.
Additionally, smart shelves equipped with RFID can detect when products are low or out of stock, so staff can restock items without manual counting.

🔐 Benefit #4: Loss Prevention and Security
RFID security, such as RFID-enabling gates at exits, can reduce theft and shrinkage. These gates trigger alarms if unauthorized items are removed without proper deactivation.
What’s more, retailers can always know where their stock items are, so nothing gets lost in the process.
Challenges and Considerations of RFID Implementation
Despite its advantages, RFID comes with challenges like cost, integration complexity, and data management.
💸 Challenge #1: Initial Costs
RFID hardware, software, and integration services can be costly upfront, especially for small retailers.
🧩 Challenge #2: Technical Integration
Ensuring compatibility with existing systems (POS, ERP) can require custom development and ongoing IT support.
📈 Challenge #3: Data Overload
RFID systems generate huge volumes of data. Without proper filtering and analytics, it’s easy to get overwhelmed.
📶 Challenge #4: Tag Interference or Misreads
Physical environments with metal or liquids can cause signal interference, affecting tag readability.
RFID Vs. Barcode: Which is Better for Your Business?
While barcodes are cheaper and easier to implement, RFID offers superior speed, range, and automation. RFID can read multiple items at once, doesn’t require line-of-sight, and integrates more easily into smart systems—making it ideal for modern retailers.
Feature | Barcode | RFID |
Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
Read Range | Short (inches) | Long (3–300 feet) |
Line-of-Sight | Required | Not Required |
Speed | Slower | Faster (bulk reads) |
Data Capacity | Low | High |
How KORONA POS Supports RFID Implementation
KORONA POS has joined forces with RFID Enabled Solutions (RES) to offer seamless RFID integration to our clients. Our system delivers real-time inventory management and reporting so you can focus on what truly matters.
Say goodbye to complex setups and exorbitant costs; with KORONA POS, you can effortlessly unlock the full potential of RFID technology. Don’t miss out on this opportunity—get in touch today!
KORONA POS has exceeded my expectations in every way. It’s a powerful, adaptable solution that has transformed our operations for the better.
-James B.
FAQs: RFID Implementation
Is there a chance RFID won’t work for me?
Yes—RFID may not be ideal if you have low inventory turnover, budget constraints, or interference-prone environments.
What sort of software will I need for my RFID system?
You’ll need an RFID platform, middleware, a secure database, and integration with your POS or ERP.
Can I setup an RFID system without software?
No—software is essential to process, store, and interpret RFID data for operational use.
How long does a typical RFID implementation take?
Depending on scale, implementation can take from 1–3 months for pilot rollouts to 6–12 months for full deployment.













