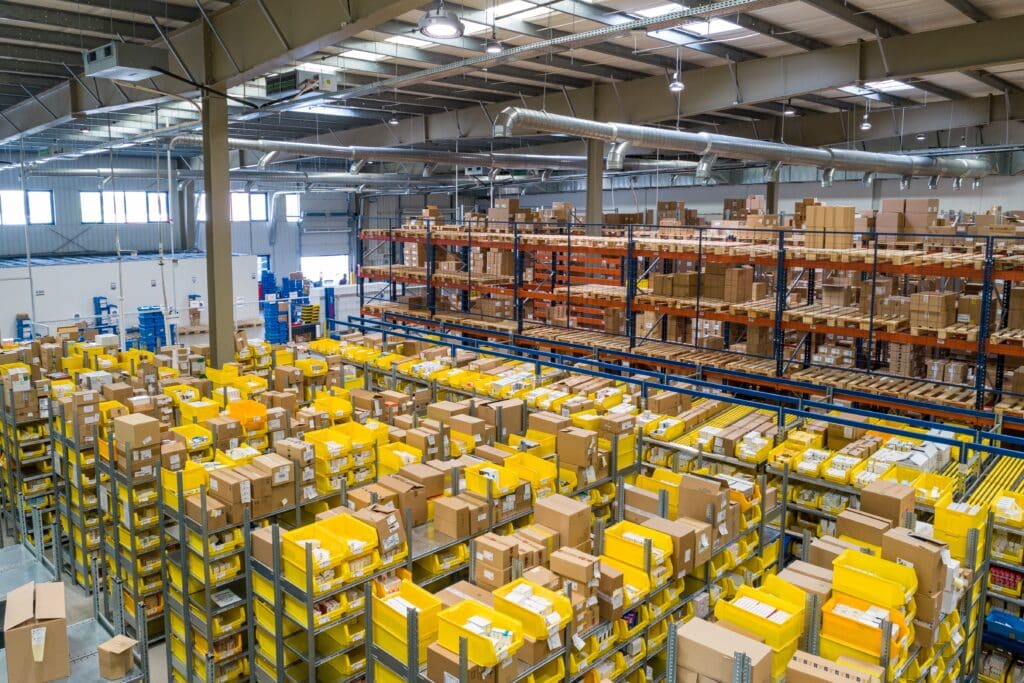

Radio-frequency identification offers a wide range of benefits across many industries. Especially for retailers, RFID is instrumental in facilitating a modern checkout. In addition, using RFID to locate items in a warehouse or storage facility is exceptionally useful.
For retail businesses with many products, RFID can help save time, labor costs, and effort. If used correctly, the technology is a powerful tracking tool. Below is a guide on how to use RFID to find items.
What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology uses small radio tags to identify and track items electronically. It can be used to locate any object or person, making it an invaluable tool for many different businesses and organizations.
With RFID, users can quickly and accurately find items. RFID technology is highly accurate, as it can pick up and read radio signals from small tags within a range of several feet. With the right tools, businesses can locate items with minimal time wasted searching for them quickly.
RFID tags are also often embedded into products, making it much easier without having to search for them manually. Finally, RFID does not require line-of-sight contact like a barcode. Thus, employees do not need to unload and unpack items to reach a barcode and scan manually.
Setting Up Your Components
RFID operates as a system. The technology has three main elements that make it work:
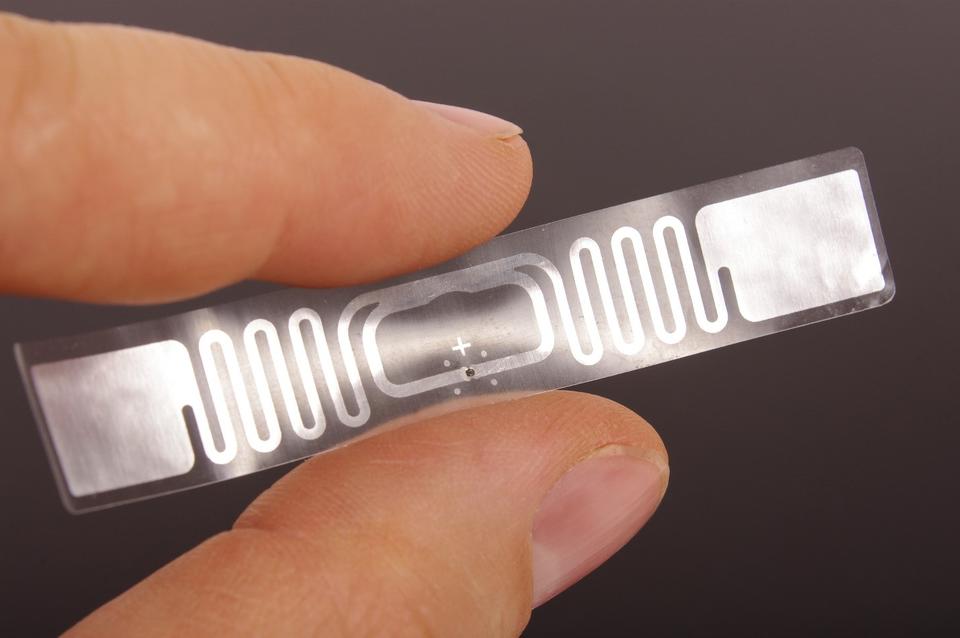
RFID Tags
Retailers attach RFID tags to individual items, boxes, pallets, or bins, much like a SKU or barcode sticker. They differ because RFID tags have small antennas that transmit digital data to readers.
Most RFID tags in retail are “passive,” meaning they do not contain batteries. Instead, radio waves emitted by a reader activate their antennas. Tags come in many different styles and sizes depending on your intended use. Most RFID tags are pre-programmed. However, small business owners can reprogram them to match the RFID system and product needs.
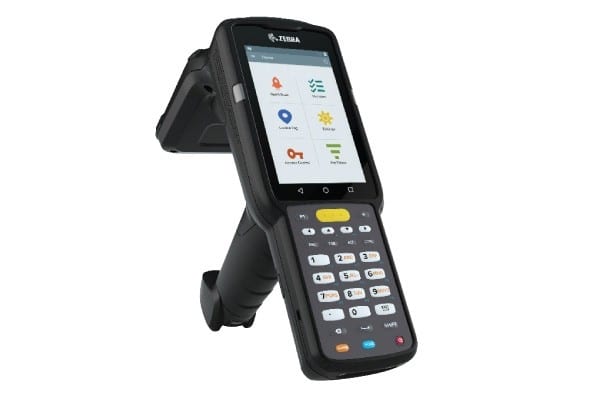

RFID Reader
The most common types of RFID readers are handheld. They often resemble barcode scanners. They will read all tags within range when pointed toward your tagged items.
Some handheld RFID readers, such as the Zebra MC3330xR, have built-in software. In the industry, people call these “mobile computing devices.”
Other readers capture the information and relay it to a smartphone or a computer via Bluetooth or another connection. This type of RFID reader is called a “sled.”

Fixed Readers
Fixed readers stay in one location, typically mounted to a wall. They can be linked with multiple antennas or smart-shelf readers to scan their assigned space accurately.
Fixed RFID reads are more helpful in tracking inventory going in and out of a warehouse or store rather than locating specific items. They provide accurate inventory numbers by accounting for all product movement in and out of a store or warehouse.
RFID Software/App
RFID inventory management requires software or smartphone applications that display and store data about products and tags. As previously mentioned, some RFID readers have integrated “mobile computing devices.” Others relay this information to a smartphone, tablet, or computer.
Either way, the software applications are necessary to store data, display information, and communicate with other integrations used in retail. These applications are also the point of contact to which you will upload information before you tag your items.
How Can RFID Be Used To Locate Items?
The easiest and most widely used way of locating an item with RFID is with handheld readers. Essentially, the reader acts like a Geiger Counter (a device used to measure radiation). The counter starts to beep or tick more rapidly as you get closer to more radioactive material.
Don’t worry; no radioactive material is needed to operate RFID. The point here is that the RFID uses a hot-cold meter that lets you know when you are getting closer to your item.
So when you are looking in a storage space or retail shelving for a specific item, you first tell your handheld reader which item you are looking for. Then, turn on the locate function and scan the room until you notice the sound picking up the frequency.
Many handheld readers also have a visual component to accompany the audial locator. This second meter helps retail or warehouse employees confirm that they are heading in the right direction.
Can You Locate Items With Fixed Readers?
Fixed readers are great for keeping track of items. For example, you may have a fixed reader on a conveyer belt that checks in wholesale products. Then, you may have another fixed reader at the other point of entry or exit that notifies your software when that tagged item has left the storage room.
In this regard, a fixed reader can be great for locating items. They tell you that an item is sitting within a specific room in your facility.
Fixed RFID readers work as an automated digital map of your overall inventory. Say you have a large operation with many storage rooms. You can go inside your database, look up an item, and see an accurate account of which rooms specific items are stored.

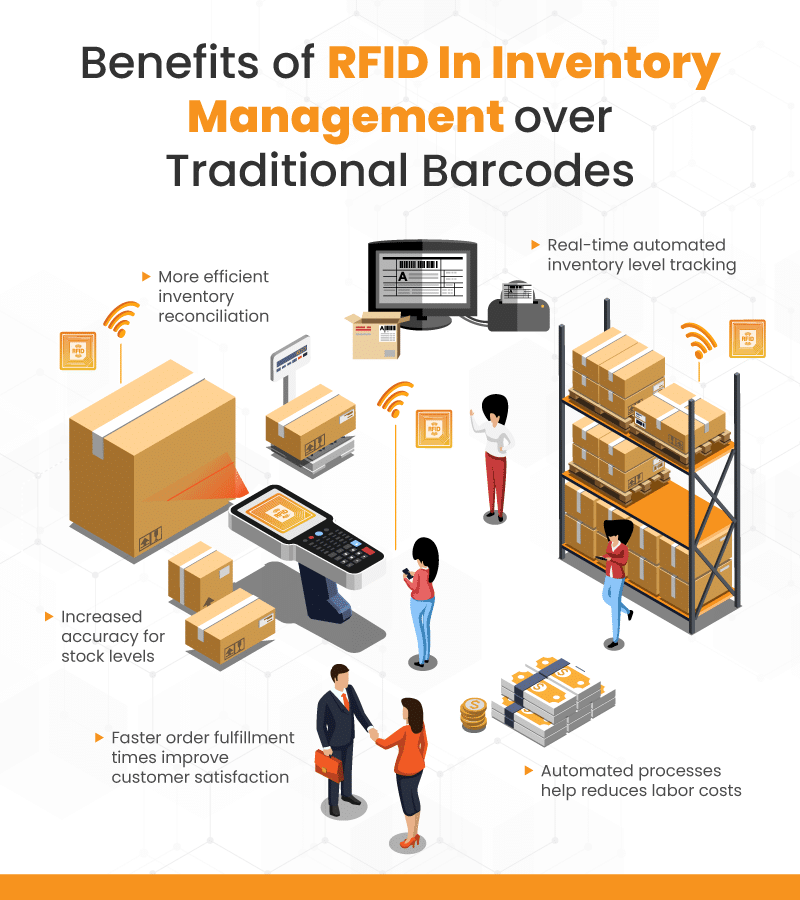
RFID Tags for Inventory: Retail Benefits
Radiofrequency can locate and track items without the need for manual line-of-site scanning. Moreover, scanners can pick up multiple items at once. Consequently, there are many benefits for retailers to use RFID tags for inventory over traditional barcodes:
- Automated tracking of inventory levels in real-time
- Increased accuracy and efficiency when managing stock levels
- Make’s inventory reconciliation drastically more efficient
- Improved customer satisfaction with faster order fulfillment times
- Reduced labor costs by automating manual processes
RFID With KORONA POS
KORONA POS is integration-ready with all of the leading retail technology. Our inventory management system is built for businesses with large, complicated product lists. This system offers an array of modern tools like ABC analysis, stock-level optimization, and auto reordering.
Connect with us today to learn how we can help you implement RFID in your warehouse or retail store. KORONA POS in-house technicians will walk you through the best hardware and software solutions for your niche and vertical. Click the button below!
FAQs: Using RFID To Locate Items
RFID location tracking is very accurate. Depending on the type of tag you use, you can get varying levels of location accuracy based on the needs of your warehouse and product. Some tags are for wide-range mass reading, while others are for finding pinpoint centimeter-specific items.
Retailers use RFID to track inventory by tagging items, bundles, or bins. These tags emit signals to RFID readers. These readers receive information without needing a direct barcode scan, tracking all inventory within range.
RFID detects location with radio waves. These waves are either emitted from “active” tags or triggered by RFID readers on “passive” tags. Through these waves, RFID sends digital information through readers into a software application that tells the user where an object is.












