RFID stands for radio frequency identification. The technology uses tiny computer chips to track products at a retail store. These chips can communicate with RFID readers through radio waves, even when embedded within product packaging or the products themselves.
As a retailer, implementing an RFID system in your store gives you visibility into your inventory in real-time. No more time-consuming manual counts or searching the backroom for missing products. You’ll instantly know what’s on hand, what’s selling, and what needs to be reordered.
This article will reveal how RFID works, its applications, benefits, and potential concerns.
What Is an RFID Tracking System?
An RFID tracking system is a wireless system that uses radio frequency waves to identify and track tags attached to objects. The system is comprised of two main components: the tag and the reader.
- RFID tags are small devices embedded with a microchip and an antenna. The chip stores the product information while the antenna transmits it to the RFID reader.
- RFID readers pick up the transmitted information from the RFID tag through radio waves, decode it, and then pass it onto a backend system for processing and action.
In other words, RFID tags store information about the object they’re attached to. The RFID reader detects the tag and reads the information when it passes through an electromagnetic zone.
For retailers, an RFID system lets you automatically identify and track individual items in your inventory. Tiny RFID tags are attached to each product, allowing you to monitor them as they move through your supply chain and store. This gives you real-time visibility into what items you have in stock, where they’re located, and which ones need to be reordered.
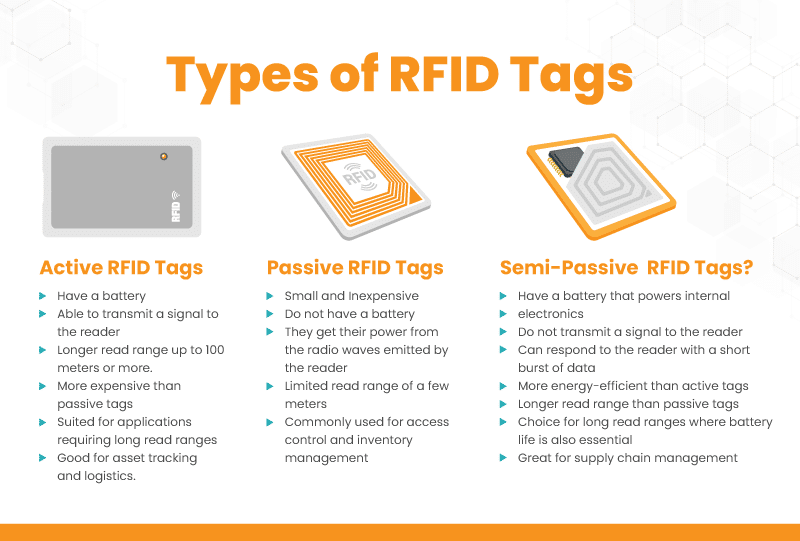
What Are The Different Types of RFID Tags?
RFID tags are devices that can be used to identify and track objects. They work by using radio waves to communicate with a reader. There are three main types of RFID tags: passive, active, and semi-passive.
Active RFID Tags
Active RFID tags have a battery, which allows them to transmit a signal to the reader. This gives them a much longer read range, up to 100 meters or more.
Active tags are more expensive than passive tags but better suited for applications requiring long read ranges, such as asset tracking and logistics.
Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags do not have a battery. They get their power from the radio waves emitted by the reader. This makes them very small and inexpensive but it also limits their read range to a few meters.
Passive tags are commonly used for access control, inventory management, and library checkout applications.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags
Semi-passive RFID tags have a battery, but they only use it to power their internal electronics. They do not transmit a signal to the reader, but they can respond to a signal from the reader with a short burst of data.
This makes them more energy-efficient than active tags while giving them a longer read range than passive tags. Semi-passive tags are a good choice for applications with long read ranges, but in situations when battery life is also essential, such as animal tracking and supply chain management.
How Does RFID Asset Tracking Work?
RFID tracking provides automatic, real-time visibility into product locations. Here is a step-by-step overview of how it works:
- RFID tags are attached to assets or placed inside product packaging or labels. Each tag has a unique identifier.
- RFID readers are set up in critical locations – warehouses, shipping zones, retail floors, etc.
- When tagged assets come within range, the RFID reader detects signals emitted by tags.
- The reader converts radio waves into digital data and passes this to a computer system.
- RFID software collates data from all readers to see which tagged products passed which read points. This provides real-time inventory visibility.
- The system instantly flags any exceptions – missing items, products that seem moving slowly, etc.
- Inventory managers then leverage analytics and reporting to optimize stock levels, identify process issues, and improve inventory accuracy.
Examples of How RFID is Used
RFID has many practical applications in retail. It provides a modern, updated way to track products and assets in a store or warehouse.
Here are some more specific examples:
Example 1: Inventory Management
RFID tags on products enable automated inventory tracking, allowing retailers to monitor stock levels in real-time and reduce instances of stockouts or overstocking. This improves inventory management and overall operational efficiency and ensures that shelves are always adequately stocked with the right products.
Example 2: Theft Prevention
RFID technology helps retailers implement anti-theft measures by tagging high-value items. RFID provides security because readers can trigger alarms if an item leaves the store without being scanned, deterring theft and reducing shrinkage.
Example 3: Omnichannel Integration
RFID facilitates seamless integration between online and brick-and-mortar retail channels. By accurately tracking inventory across all channels, retailers can offer services like buy online pick up in-store (BOPIS) or ship-from-store.
This provides customers with flexible shopping options while optimizing inventory utilization, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
Inventory management headache?
KORONA POS makes stock control easy. Automate tasks and get a clear picture of your entire inventory.
The Importance of RFID Asset Tracking for Retail Outlets
For retailers dealing with a large, constantly changing inventory, RFID tracking brings many benefits:
Real-Time Visibility
RFID tags allow you to scan entire shelves or storerooms of products simultaneously to get an instant snapshot of your inventory. Within seconds, you’ll know exactly what products you have on hand, their locations, and how much stock remains of each item.
This real-time visibility ensures you don’t run out of popular products and can spot any shipping or receiving errors immediately.
Product Protection
As touched upon earlier, RFID also helps combat loss from theft or product expiration with asset protection. RFID readers positioned at exits can detect if unpaid merchandise is being removed from the store.
You’ll also get alerts if any products have remained on the shelves past their expiration or “sell by” dates so you can remove them promptly.
Improved Customer Service
With an RFID system, your sales associates have the product information they need right at their fingertips to assist better customers. They can instantly look up stock levels, product details, and substitute options if something is out of stock.
The ability to provide fast, accurate answers and recommendations gives your customers a great shopping experience.
Labor Cost Savings
RFID reduces the need for employees to check and record inventory manually. Once the RFID tags and readers are in place, tracking is automated. Workers are freed up to focus on helping customers instead of the tedious task of counting products and scanning barcodes.
Gain Business Insights
The data from your RFID system provides valuable insights into your business. You’ll see how customers move through your store, how long they spend in different departments, and which products they’re most interested in.
This helps you optimize product placement, staffing, and marketing. You can also analyze trends to spot seasonal peaks, anticipate demand, and make better purchasing decisions.
RFID Tracking vs. Barcode Tracking
Both RFID and barcodes identify items, but RFID offers some key advantages:
- Hands-free scanning – RFID readers automatically detect tags without needing direct line-of-sight. Barcodes require manual scanning of each item.
- Unique identity – RFID tags have a distinct ID, while barcodes only identify product type. This enables tracking individual items.
- Data capacity – RFID tags can store more data like manufacture date, expiry, etc. Barcodes are only able to contain a product reference.
- Read range – RFID can be read from around 10 feet away, while barcodes need proximity scanning.
- Durability – RFID tags are more durable and resistant to dust, dirt, and moisture. Barcodes and barcode scanners can get damaged easily.
- Cost – RFID implementation is much more expensive than that of barcode scanning. For high-volume retailers, the cost of RFID tagging is typically worthwhile, but it must be a major consideration nonetheless.
Industries That Use RFID Asset Tracking
RFID asset tracking is extensively deployed in various retail verticals. In apparel retail, for example, RFID tags on clothing items enable accurate inventory visibility, reducing stockouts, and enhancing omnichannel operations.
Grocery stores utilize RFID to monitor perishable goods, ensuring freshness and minimizing waste. Electronics retailers benefit from RFID in tracking high-value items, preventing theft, and optimizing stock levels.
RFID technology is also used in the Cannabis industry. As soon as a plant reaches maturity, it must be entered into state compliance systems using individual RFID tags.
Moreover, RFID enables product authentication and anti-counterfeiting measures in luxury goods retail, safeguarding brand reputation.
RFID technology also enhances the efficiency of checkout processes, enabling faster transactions and reducing queuing times.
RFID Self-Checkout Technology: The Future of Retail Checkout
RFID is bringing the next evolution in automated checkout technology – RFID self-checkout kiosks. Walmart, Amazon, and other major retailers have already implemented RFID self-checkout in hundreds of stores.
The way it works is simple: all items have RFID tags. Instead of scanning individual barcodes, customers simply place all purchased items on an RFID reader pad. The RFID reader instantly detects every item and displays their its prices and description on a screen. Customers can validate the items, make payments right there, and leave without needing any checkout assistance.
RFID self-checkout provides many benefits compared to barcode-based systems:
- Faster checkout – Entire baskets are processed rapidly instead of individual scans. Overall time per transaction is significantly lower than traditional checkout lanes.
- Better accuracy – RFID reads tagged items perfectly every time, reducing misses and false scans.
- Enhanced security – The system automatically detects unpaid items leaving the store.
- Additional data – Item counts, basket metrics, and other data enable targeted promotions and recommendations.
- Improved customer experience – Self-service RFID checkout empowers shoppers, reduces wait times, and creates a frictionless exit process.
With RFID costs falling and technology advancing, RFID-based automated checkout will soon become ubiquitous across retail stores. It creates a win-win – improving inventory accuracy for retailers while providing customers with a faster and hassle-free checkout experience.
Implementing RFID Technology With KORONA POS
KORONA POS is a cloud-based point of sale system (POS system) that helps businesses of all sizes streamline their operations. One of the ways KORONA POS can help retail outlets is by integrating RFID technology with its self-checkout solution.
Customers can simply place their basket or cart under the RFID reader, and all items in their basket will be automatically scanned and added to their checkout total.
There are several notable features of the KORONA POS self-checkout kiosk:
1. Use RFID for Faster Checkouts: The self-checkout stands use RFID, which means quicker checkouts and no double-scanning mistakes.
2. Self-service ticketing for events and attractions: This is great for events and places needing tickets. Customers can easily buy tickets using these touch-free kiosks.
3. Good for shops and fast food: These checkout stands are handy for many businesses, from retail stores to QSRs and admissions. They help shorten lines and lessen the work for staff.
KORONA POS seamlessly integrates self-checkout kiosks with the backend retail management system. All transaction data, sales metrics, and RFID inventory reads are synced in real-time. This provides retailers with a single unified view of all checkout data.
KORONA POS has been a huge game changer for my overall profitability. Implementation was seamless and painless! The support staff is great and always ready to help. Had I known it would be this easy, I would have made the switch sooner!
-Kristen L.
FAQs: RFID Tracking System
RFID is used for tracking by attaching tags with unique IDs to assets and using readers to detect those tags as assets move through set locations.
RFID tracks location by setting up readers at key chokepoints and using them to detect which tagged assets are passing by those readers.
An RFID tracker is an RFID reader that automatically identifies and tracks the movement of assets equipped with RFID tags.
RFID Tracking System: Conclusion
Implementing an RFID system for your business will boost efficiency, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance the customer experience. While the initial investment may seem high (RFID tech is not cheap), the long-term benefits to your bottom line and business processes will make RFID worth the cost.
For high-volume retail, RFID is becoming a necessary upgrade from manual barcode scanning to keep up with omnichannel commerce. RFID-based innovations like self-checkout are the future of retail checkout.
With ROI driven by reduced stockouts, better inventory control, and improved staff productivity, RFID is a wise long-term investment to transform inventory management.
Click below to learn more about how KORONA POS can help your business roll out its new RFID solution.











