Struggling to make sense of your retail POS data? Whether it’s customer preferences, sales trends, or inventory management, understanding your POS system can be overwhelming — but it doesn’t have to be.
In this guide, we’ll show you exactly how to unlock the full potential of your POS system so you can make smarter decisions and boost your competitive edge. You’ll learn practical strategies to analyze your data, turn insights into action, and streamline operations — so by the end, you’ll know exactly how to leverage your POS data for real business results.
Key Takeaways:
- Every POS system collects large amounts of transactional data after the customer has paid. This data helps retailers streamline their operations and inventory management.
- There are several key types of POS data that, when analyzed, can streamline your retail operation’s decision-making.
- Best practices like centralizing data, regularly backing up information, and maintaining robust security protocols are essential to ensuring the accuracy and safety of your POS data.
What is POS Data?
POS data is the information collected at the point of sale. With features like POS reporting and analytics, businesses can use their POS systems to track data like sales metrics, inventory turnover, employee performance, key performance indicators (KPIs), and much more.
There are seemingly infinite possibilities when it comes to leveraging and analyzing POS data. Programs like KORONA POS offer tools to unlock the full potential of this data so you can enhance your decision-making, retail operations, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Benefits of POS Data Analytics for Retailers
Leveraging POS data analytics allows retailers to operate more efficiently, enhance customer experiences, and stay competitive in a fast-changing retail environment. Here are the key benefits, backed by real-world insights:
1. Data-Driven Decision-Making
POS analytics provides real-time insights into sales, inventory, and customer behavior.
Key advantages:
- Improve operational planning
- Forecast demand using historical sales trends
- Optimize pricing and promotions
- Reduce inventory waste
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
Retailers can personalize shopping experiences using POS data.
Key advantages:
- Track customer purchase history to recommend products
- Design loyalty programs that increase repeat visits
- Tailor promotions to individual preferences
- Improve overall customer satisfaction
- Example: Reddit users note that small businesses using POS-driven loyalty programs see higher return rates and more frequent purchases.
3. Competitive Advantage
POS analytics enables retailers to respond faster to market changes than competitors.
Key advantages:
- Identify emerging product trends before competitors
- React quickly to inventory shortages or surpluses
- Optimize staffing and sales strategies based on data
- Make strategic decisions that boost long-term growth
4. Operational Efficiency
Data analytics reduces manual tasks and streamlines workflows.
Key advantages:
- Automate reporting and inventory tracking
- Reduce human error in orders and stock management
- Save time for staff to focus on customer service
- Improve supply chain coordination
5. Marketing Effectiveness
POS data informs more targeted marketing campaigns.
Key Takeaways:
- Increase conversion rates through data-backed decisions
- Segment customers based on purchase behavior
- Test promotions and track ROI in real time
- Launch seasonal campaigns optimized for top-selling products
9 Types of POS Data to Analyze
Understanding and analyzing specific types of POS data can empower retailers, putting them in the driver’s seat of their retail business. Here are nine POS data types that can give you the control and confidence to make meaningful business decisions:
1. Sales Data
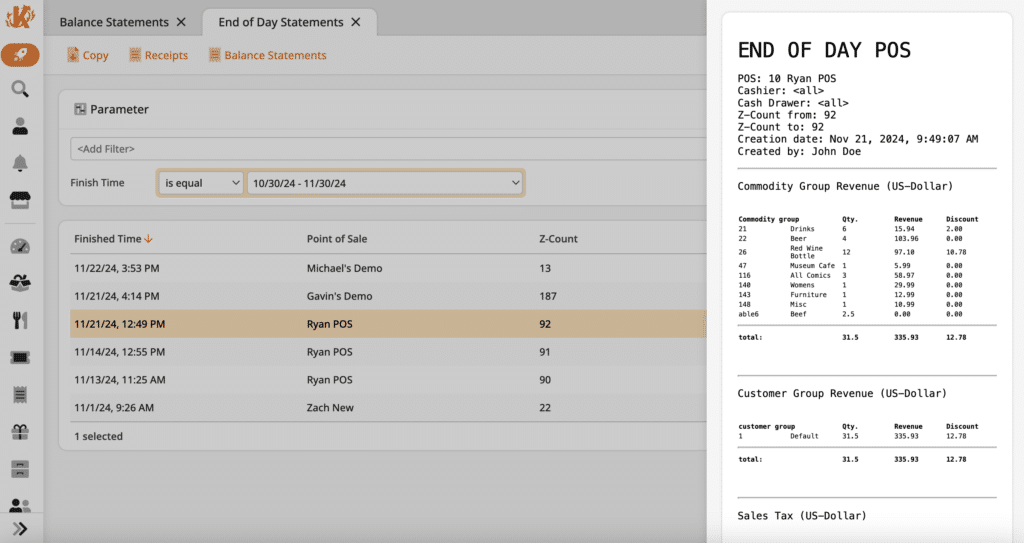
Retailers can track sales data to understand daily, weekly, and monthly sales trends to identify best-selling products and forecast consumer demand. Sales data fits neatly into retail daily sales reports or inventory spreadsheets, which help retailers make data-driven decisions about inventory and pricing strategies.
2. Transaction Data
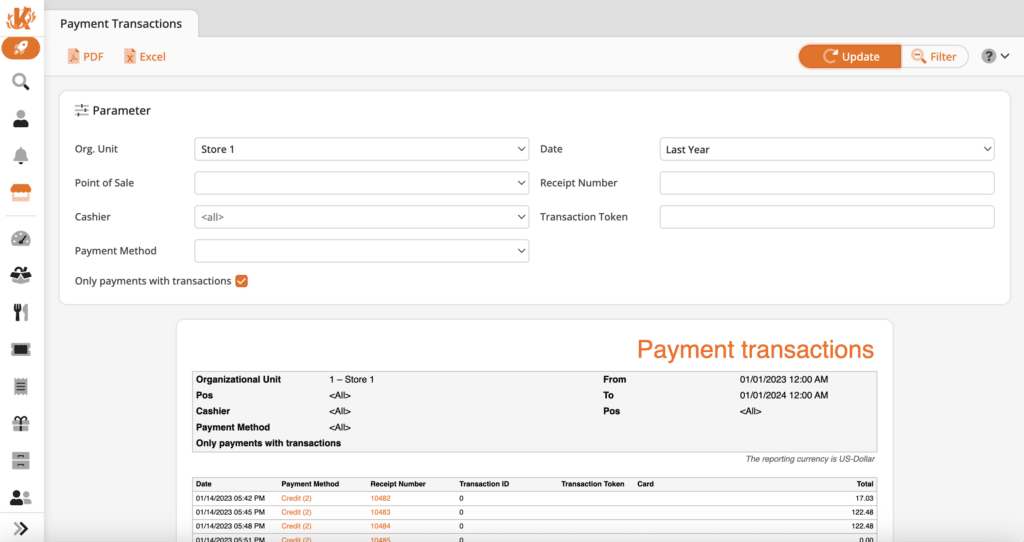
Transaction data shows users the transaction amount, payment type, and transaction type per sale. Knowing these data enables retailers to confidently refine their sales strategies and enhance customer engagement and experience in hyper-specific ways.
3. Product Data
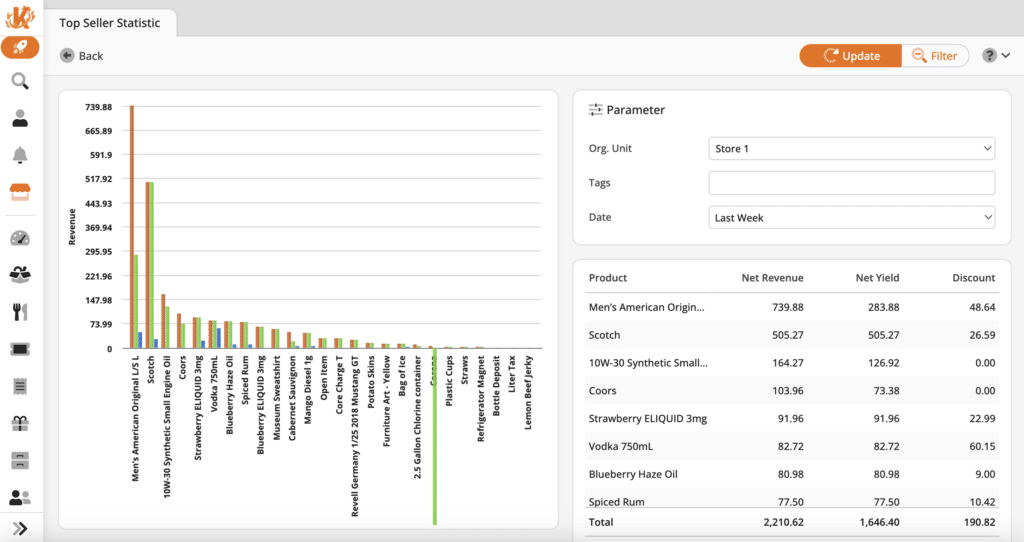
Product data is the information obtained about each product item during a transaction. It looks at what customers bought, the quantity purchased at a time, the amount spent on the product, and what it was purchased with.
Retailers can use this information to understand sales value (how successful a product is over time) or how pricing affects a product’s popularity.
4. Customer Data
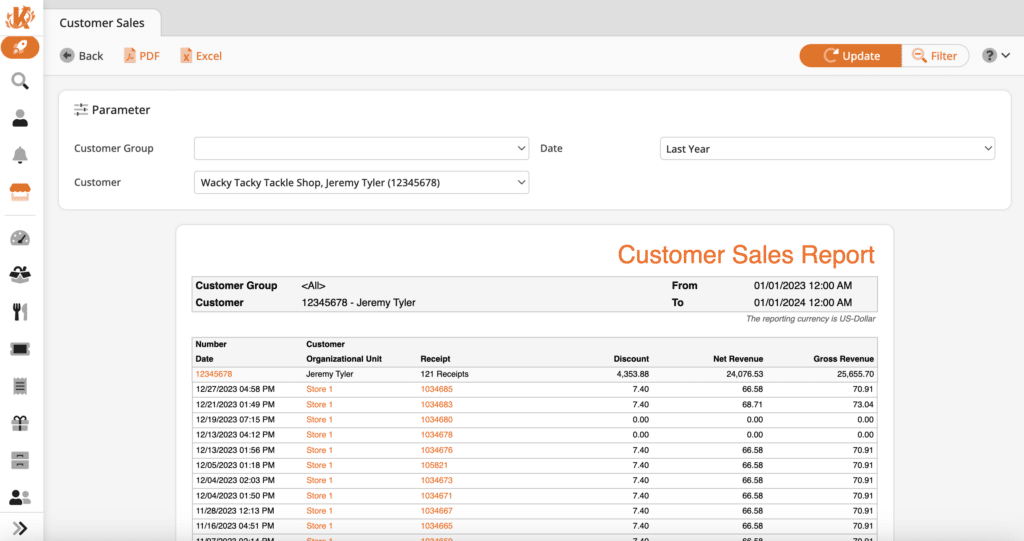
Retailers can use their POS system to analyze customers’ buying behavior, especially if they’ve signed up for a loyalty program. Customer data is helpful to retailers in targeting promotions to the right people at the right time and refining marketing strategies.
5. Peak Hours Data
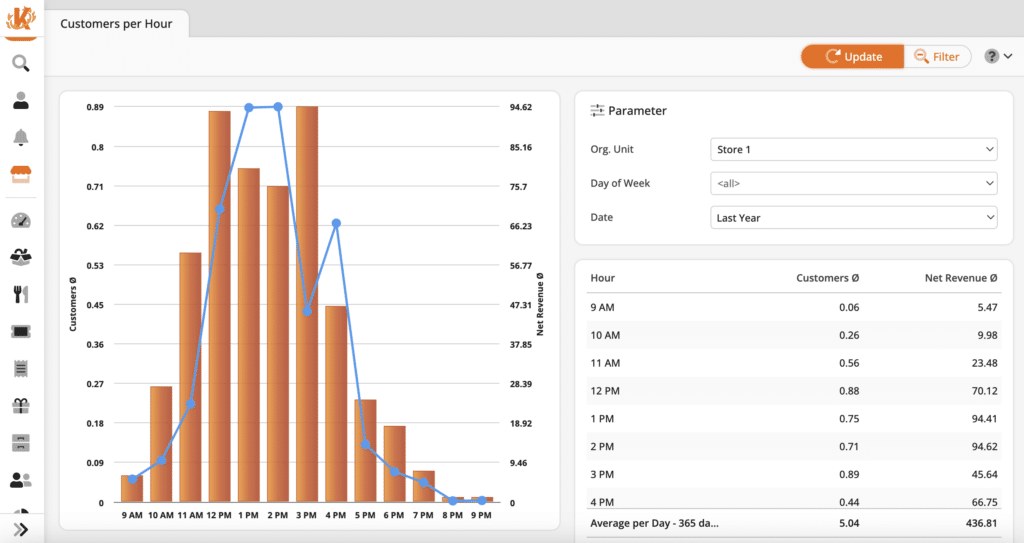
Peak hours data shows retail stores when their store has the highest foot traffic or when peak sales periods occur. Business owners can leverage this data to look at the time of sale, make decisions about staff scheduling, and optimize their retail inventory management system.
6. Location Data
POS data can tell retailers exactly where a sale was made. This information can be as specific as a country, region, town, retail store, and even individual POS checkout station.
Location data helps retailers understand how sales perform by location and customer level. It also paves the way for targeted marketing strategy with a POS system, staffing decisions, or product promotions in specific store areas.
7. Discount and Promotion Data
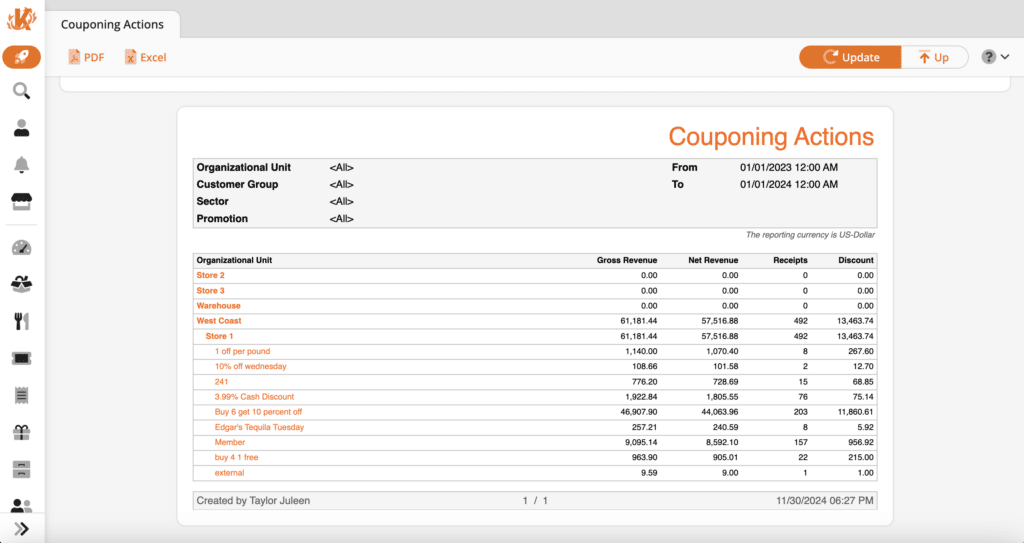
POS users can use discount and promotion data to track retail sales performance, discounts, and promotions to evaluate their return on investment (ROI).
Discount and promotion data helps retail stores identify which offers resonate with customers by driving sales and which need adjustments.
8. Employee Performance Data
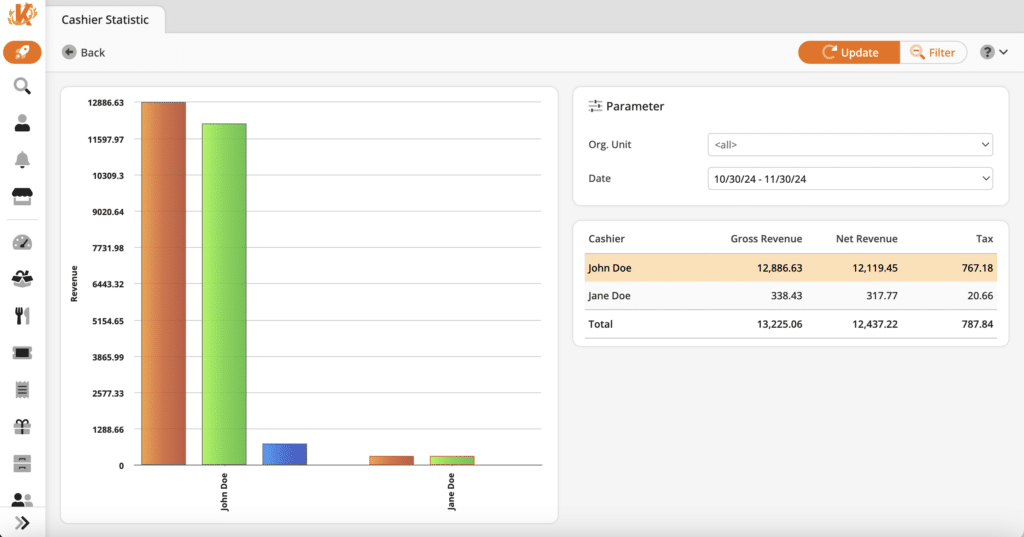
POS data enables retailers to track sales performance and identify top-performing employers. It can track metrics like individual sales, upselling success, transaction times, and customer satisfaction ratings.
Analyzing employee performance data helps retail stores identify top performers, address training needs, and align employee incentives with business goals. By leveraging this data, businesses can boost productivity and create a more efficient workforce.
9. Refund and Return Data
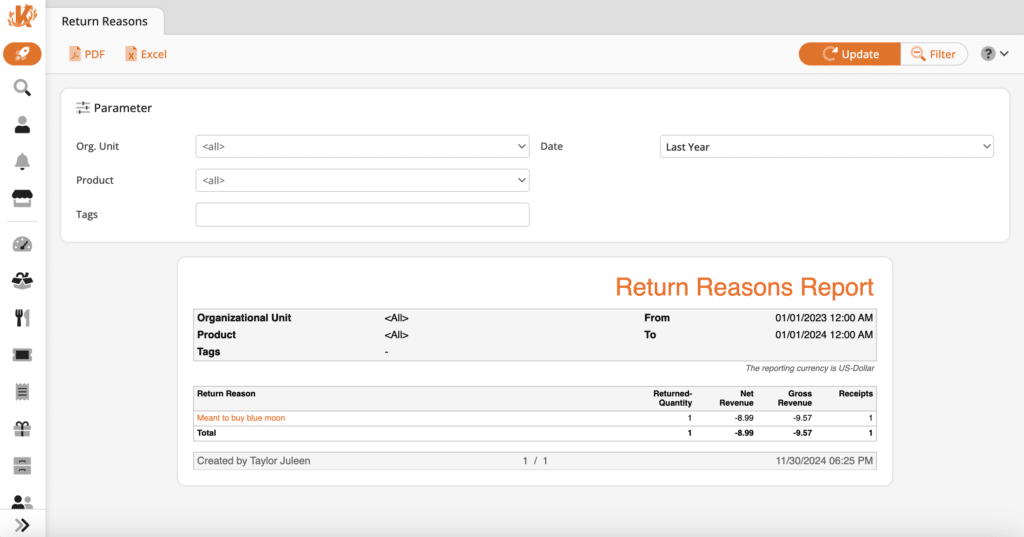
Refund and return data gives retailers deep insights into returned product patterns, why customers seek refunds, and the behavior associated with these transactions.
This data helps retailers identify which items are defective, have sizing inconsistencies, or have misleading product descriptions. Refund and return data helps retail stores reduce future returns, improving quality control and customer trust.
Discover Advanced Analytics and Custom Reports
Speak with a product specialist and learn how KORONA POS can power your business needs.
Examples of POS Data Analysis
POS data are not abstract concepts; they’re applied tools businesses use to streamline operations. Let’s take a look at POS data in action through some real-world examples:
Example 1: Inventory Optimization
Inventory Optimization
A boutique clothing retailer noticed through their POS system that certain seasonal items were overstocked while others sold quickly.
They identified the mismatch between customer preferences and purchasing strategy using inventory data. Using these insights, the retailer adjusted their orders for the following season, prioritizing popular items and reducing surplus stock levels. This resulted in a 20% decrease in carrying costs and a 15% increase in overall retail sales during the next seasonal period.
Example 2: Customer Loyalty Programs
Customer Loyalty Programs
A local coffee shop leveraged POS data to analyze customer purchase frequency and preferences. They found that customers who bought specialty drinks were more likely to return when loyalty rewards were offered.
By introducing a tailored rewards program offering a complimentary specialty drink after ten purchases, the shop increased customer retention by 30% within six months. The program also boosted average transaction values, as some customers opted for the higher-priced specialty drinks to engage in the rewards program.
Example 3: Employee Performance
Employee Performance
A mid-sized electronics store used POS data to track each employee’s sales performance and transaction times. The data revealed that employees with higher accessory upsell rates also had shorter transaction times.
Management implemented a training program where top-performing employees shared their strategies, leading to a 15% increase in accessory sales, improved sales efficiency, and camaraderie among the team.
POS Data Management Best Practices
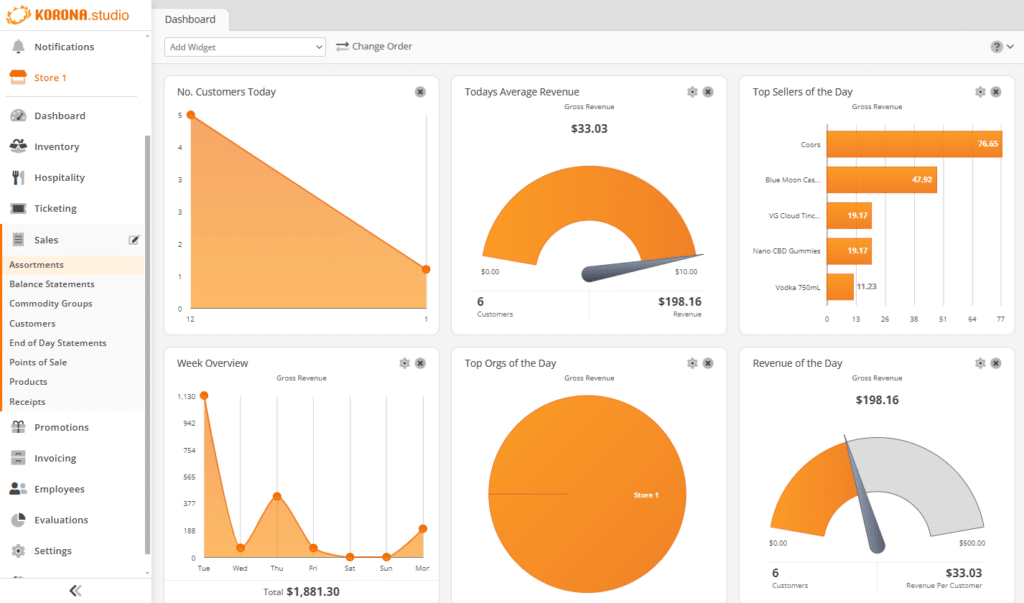
Without proper POS data management, businesses risk losing important sales information or falling victim to data breaches. Let’s take a look at which POS data management best practices can help retailers manage their data securely and effectively:
Best Practice 1: Centralize Data Storage
Keep all your POS data in a single, secure system for easy access across locations and departments. Centralized data reduces errors, improves reporting, and helps you spot trends faster.
PRO TIP!
Use cloud-based POS systems like KORONA POS to consolidate sales, inventory, and customer data. Ensure all locations feed into the same database for accurate multi-store reporting.
Best Practice 2: Regularly Backup Data
Ensure that all your POS data is backed up frequently on secure cloud servers or external drives. Data backups prevent loss due to system failures or cyberattacks.
PRO TIP!
Cloud-based POS systems like KORONA POS allow automated backups and easy restoration, giving retailers peace of mind.
Best Practice 3: Maintain Strong Data Security
Secure sensitive customer and sales data with encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access controls.
PRO TIP!
Audit your system regularly for vulnerabilities, educate staff on best practices for handling customer data, and limit access to sensitive information based on employee roles.
Best Practice 4: Regularly Organize Your Data
Regularly review, clean, and standardize your POS data to maintain accuracy. Clean data improves decision-making, streamlines reordering, and ensures reporting is reliable.
PRO TIP!
Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize product SKUs and names. Then, schedule monthly or quarterly data audits.
Best Practice 5: Use Reporting Tools
Turn raw data into actionable insights by using built-in or third-party analytics tools. KORONA POS offers customizable dashboards to track sales, optimize inventory, and evaluate promotion success in real time.
PRO TIP!
Track key metrics like sales trends, inventory levels, and customer behavior. Use visual dashboards for quick, actionable insights. Then, test different reporting formats (daily, weekly, monthly) to find what drives decisions.
Get started with KORONA POS today!
Explore all the features that KORONA POS has to offer with an unlimited trial. And there’s no commitment or credit card required.
Final Thoughts
POS data is a powerful tool that helps retailers optimize sales, inventory, employee performance, and customer engagement. By implementing best practices in POS data management and analytics, retailers can make accurate, data-driven decisions that improve efficiency and competitiveness.
When choosing a POS system, look for essential features such as centralized data management, real-time analytics, automated backups, customer relationship tools, inventory optimization, and a user-friendly interface — all of which KORONA POS provides. These features streamline operations, protect your data, and give actionable insights, helping retailers harness the full potential of their POS systems and thrive in a fast-paced market.
FAQ
Can I Transfer POS Data to Another POS?
Yes, most modern POS systems allow data migration via export-import functions. Make sure there’s compatibility between systems to avoid errors.
What is panel data vs POS data?
Panel data tracks the same subjects (like customers, households, or stores) over time to analyze trends and changes, while POS data records individual sales transactions at the point of sale, capturing information like items sold, prices, and customer behavior in real time.
How Can POS Data Integrate with Other Business Software?
POS data can integrate with accounting tools, inventory management systems, and CRM platforms. While you can do this manually, POS software like KORONA POS makes all the above achievable and accessible from one place.











